Quantum Computing’s Impact on IP Rights & Patent Law: Navigate Now!
As we dive into the riveting implications of quantum computing, it can feel like standing at the edge of a technological cliff—breathless and uncertain about what lies beneath. Quantum computing is not just a breakthrough in technology; it's a seismic shift influencing how we think about intellectual property rights and patent law. In this era of rapid advancements, our legal frameworks must adapt, challenging existing paradigms and inspiring exciting innovations.
The Intersection of Law and Quantum Technology

Quantum computing heralds an age where computational capabilities transcend classical limits, enabling complex problem-solving at unprecedented speeds. This evolution heralds not only new opportunities for innovation but also profound challenges in intellectual property (IP) rights and patent law. For businesses and creators, understanding this intersection is crucial for safeguarding their unique ideas and technologies.
The Basics: What is Quantum Computing?
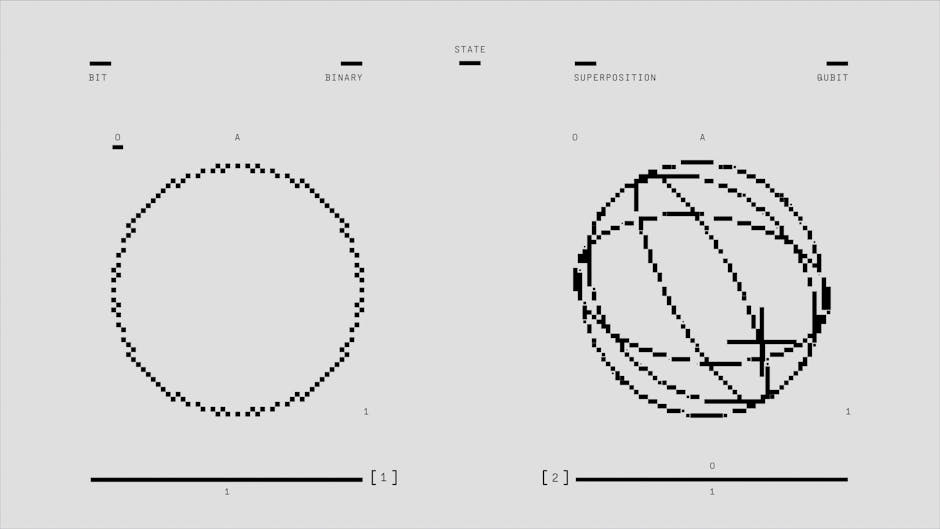
In layman's terms, quantum computing utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations at speeds unattainable by traditional computers. Instead of bits—0s and 1s—quantum computers use qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously, enhancing calculation power exponentially. This revolutionary change opens doors to fields such as cryptography, materials science, and artificial intelligence.
But with these doors come inevitable legal questions: How do we protect innovations that can be developed or deciphered through quantum computing? The stakes are high, and navigating this quantum legal landscape demands attention.
Current Laws vs. Emerging Technologies

The current legal frameworks surrounding IP rights and patents were largely established before the advent of quantum technology. Existing legal paradigms often struggle to accommodate the rapid pace of technological progress. For instance, traditional patent laws require clear descriptions of how an invention works. In quantum computing, the complexities of superposition and entanglement can make these descriptions challenging to formulate.
Case Studies in Quantum Innovation

Consider the work of tech giants such as IBM and Google, where innovations in quantum algorithms have led to breakthroughs that could transform industries. The legal implications of these developments are staggering. If IBM develops a quantum algorithm that redefines cryptography, how do we determine ownership? What if a startup, unaware of the groundbreaking nature of a principle it utilizes, inadvertently infringes on IBM's intellectual property?
These scenarios illustrate the importance of adapting intellectual property laws to ensure fair protections are in place, allowing innovators to thrive without the fear of unwarranted litigation.
Copyrights: The New Frontier

As quantum computers become more sophisticated, they will inevitably usher in novel creations—art, music, software—that challenge our traditional understanding of copyrights. We need to ask: Who owns the rights to a digital piece created by a quantum algorithm? Is it the coder, the machine, or perhaps the entity that owns the quantum computing infrastructure?
As a relevant example, consider the legal maze surrounding AI-generated art. The concept of authorship is rapidly changing, compelling lawmakers to revisit regulations that govern ownership and rights surrounding existing works.
Patents and Quantum Computing: A Complex Relationship

Patent law requires "full disclosure" of an invention's workings, which can create tension when it comes to quantum technologies. Given their complex nature, what happens if key elements of a quantum-based invention are not patentable due to their theoretical basis?
Navigating the Quantum Patent Process

-
Determine Novelty: Inventors must establish that their quantum innovation is novel compared to prior art. This determination can be complex, as quantum technology often builds upon existing theories.
-
Enablement: Legal requirements mandate that patent applications must enable those skilled in the art to replicate the invention. This is particularly challenging in quantum technology, where foundational theories may be abstract.
-
Claims Construction: Precision in drafting claims is crucial. Given the intricate nature of quantum mechanics, legal definitions must accurately reflect the innovative aspects of a quantum invention without losing clarity.
International Perspectives: A Global Challenge

As quantum computing continues to push boundaries, the global nature of innovation presents a myriad of legal challenges. IP rights vary significantly from country to country, and harmonizing regulations internationally is paramount to fostering global collaboration.
The Role of International Treaties

Treaties such as the Establishment of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) lay the groundwork for IP protection across borders. However, these treaties must evolve to account for the unique challenges posed by quantum advancements.
Attention must also be paid to emerging economies where patent systems may not be fully developed, potentially resulting in unequal protections for creators and innovators.
Ethics and Quantum Computing in Law

As with any emerging technology, ethical considerations come into play when discussing the implications of quantum computing on legal standards. The potential for quantum computing to alter not just processes but also public perceptions of intellectual property raises critical ethical questions.
The Fairness Perspective
As discussed in our article on AI in legal settlements, fairness remains at the forefront of legal discussions. How do we ensure equitable access to quantum advancements? Who gets credit, and is this credit commensurate with contribution in an age of shared technologies? Navigating these ethical terrains is crucial for fostering a just legal landscape.
Potential Legal Reforms: A Necessary Evolution

Given the rapid evolution of quantum technologies, a proactive approach to legal reform is essential. Collaboration among lawmakers, technologists, and legal experts will be paramount in formulating flexible frameworks that can adapt to future developments without stifling innovation.
-
Establishing Quantum-Specific Frameworks: Most critical is the acknowledgment of quantum computing as its legal domain, separate from traditional computing laws.
-
Creating Clear Guidelines: Developing clear guidelines around the patenting of quantum algorithms and technologies can prevent future conflicts and protect rights effectively.
-
Open Source and Collaboration: Encouraging open-source collaboration can stimulate innovation while establishing fair credit mechanisms among contributors.
Future-Proofing Legal Strategies

The road ahead requires not only adaptation but also foresight. Legal professionals must educate themselves about quantum technologies and their implications, positioning themselves as thought leaders in this intricate space.
Continuing legal education, interdisciplinary collaboration, and awareness of emerging trends will be invaluable for legal practitioners. The nuances of quantum advancements will demand an agile approach to ensuring rights are protected while fostering an environment ripe for innovation.
Integration with Other Emerging Technologies
Finally, quantum computing does not exist in isolation. The interplay between quantum advancements and other technologies—like AI, blockchain, and cybersecurity—poses additional challenges to legal frameworks.
For example, the legal implications of using quantum computing to enhance AI technology are profound. As discussed in our piece on AI-driven mediation, understanding how these technologies overlap is essential for building durable legal protections in interconnected domains.
The Interdependence of Future Technologies

The increasing interdependence of quantum computing and other emerging technologies underscores the need for a comprehensive and cohesive legal strategy. Awareness and expertise in intertwined domains will yield innovative legal solutions moving forward.
Final Thoughts
Navigating the quantum legal landscape is akin to scaling a mountain; the journey may be challenging, but the view from the top is worth the effort. As businesses, innovators, and legal professionals grapple with the implications of quantum computing on intellectual property rights and patent laws, proactive adaptation will be key.
As we embrace this brave new world, a shared understanding among stakeholders—including inventors, lawmakers, and legal practitioners—will ensure that innovation flourishes in an atmosphere of fairness and integrity.
Next Steps
For those interested in deepening their understanding of related legal landscapes, exploring articles on the legal implications of AI-generated art or the effects of blockchain on intellectual property laws can provide additional insights. Furthermore, staying abreast of legal reforms and innovations in quantum technology will equip you to navigate the challenges and seize opportunities in this fascinating frontier.




